This article is about Pyrometers. Types of pyrometers (Resistance Pyrometers, Optical Pyrometers, and Radiation Pyrometers) are also explained in detail.
Pyrometers
Pyrometers Instruments that measure high temperatures by
running electricity are called pyrometers. It can successfully record or display
the temperature in all places where other thermometers can be used under
certain conditions.
Types of Pyrometers
There are four types of Pyrometers.
- Resistance Pyrometers
- Thermo-Electric Pyrometers
- Radiation Pyrometers
- Optical Pyrometers
1. Resistance Pyrometers
Resistance pyrometers work on the principle that when the temperature of a metal changes, so does the resistance of that metal. For example, if the temperature of a resistance wire made of platinum is changed, its resistance also changes with the ratio of temperature. Thus the change in resistance is measured by the change in temperature.
Construction of Resistance Pyrometer
In the resistance pyrometers, a thin insulated platinum wire
is winded on the frame made of mica. Which is enclosed inside a tube made of
porcelain or fuse desselica. To make this tube more secure, it is enclosed in a
steel tube. (a).
 |
| Pyrometers |
Figure (b) shows the interconnection of the Whetstone Bridge
network and thermometer for measuring temperature. The measuring circuit is connected
to the copper wire at a suitable distance from the pyrometer. Changing the
temperature also changes the resistance of a copper wire or leads. Which may
cause measurement errors. To correct this error, two more wires equal to the
size of the wires are pulled from the other arm of the bridge circuit and
placed inside the thermometer in the form of a loop. But it is not paired with
resistance wire.
The change in temperature causes the resistance of both the
original lead and the compensating lead to change over time. Since the two
towers are on opposite sides of the network. Therefore, the possibility of
error disappears automatically. Also called Platinum Wire Practicing. So that
its resistance remains constant even after prolonged use. And prevent changes
caused by the strain during use. (The process of cooling metal at a certain
rate after heating is called annealing).
 |
| Resistance Pyrometer |
Working Principle of Resistance Pyrometers
These pyrometers are used with the common type of Whetstone
Bridge. If the resistance of the thermometer is low then Calvin Double Bridge
is used instead of Whetstone Bridge. The resistance of the thermometer changes
with changing temperature.
P and Q are two identical arms of the bridge network. The
third arm of the bridge consists of a variable resistance R and compensating
leads. The thermometer's platinum resistance coil is attached to the fourth arm
of the bridge. There is a slide wire between the third and fourth arms. The
bridge is balanced by moving the sliding contact back and forth. For this
purpose, the calibration of the slide wire in specific bridges should be done
in such a way that it directly reflects the temperature.
When the bridge is balanced, very little current passes through the galvanometer G due to the difference in resistance. The current passing through the galvanometer depends on the change in the resistance of the thermometer as the temperature changes. The deflection of the galvanometer is therefore calibrated in such a way that it reflects the temperature directly on the scale in degrees Celsius.
Applications of Resistance Pyrometers
- Resistance pyrometers are used to measure temperatures up to 900°C (sometimes up to 145°C with intervals).
- They are more expensive than thermoelectric pyrometers. However, provide more accurate readings.
Thermo-Electric Pyrometers
Working Principle of Thermo-Electric Pyrometers
Thermoelectric pyrometers operate under the See-Back effect.
According to this principle, if the ends on one side of two different metals
are joined together and heated, it is called a hot junction. EMF is produced
directly proportional to the difference in temperature at both the junctions.
If two leads are taken out of the cold junction and connected to the indicating
instrument, i.e. the galvanometer, then this instrument will show the changes
in the temperature of the heart junction as compared to the cold. The
deflection of the galvanometer is proportional to the EMF of the
thermoelectric. The galvanometer is calibrated in such a way that it reflects
the temperature directly. This method is used to measure high temperatures.
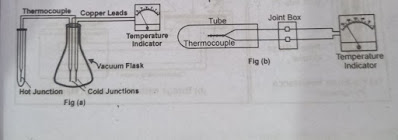 |
| Thermo-Electric Pyrometer |
Construction of Thermo-Electric Pyrometers
This pyrometer uses a thermocouple of iron Constantine
material. A sheath is used around the hot junction to protect the thermocouple.
The sheath is made of steel or nickel chrome. If a pyrometer is to be used to
measure high temperatures, a porcelain or quartz sheet is applied. Sheets of
Alundum material are used to measure extreme temperatures. Wires from 0.02
inches to 0.1 inches in diameter are commonly used to make thermocouples. The
junction of the thermocouple is made by fusing the dots or twisting both.
 |
| Thermo-Electric Pyrometer |
Applications of Thermo-Electric Pyrometers
- Thermoelectric pyrometers are used for measuring temperatures of 80 to 2600 C. They measure temperature very quickly or with very little lag.
- These resistors do not provide more accurate readings than a pyrometer.
- Therefore, they are used on a commercial basis for general purposes. However, they are relatively cheap.
Radiation Pyrometers
A radiation pyrometer is used to measure temperature from
1200 C to 3500°C. It is not easy to place a measuring instrument inside a hot
body or furnace to measure such a high temperature. Therefore, these pyrometers
are used to determine the temperature of a source that is located away from the
source but operates on the basis of heat radiated from the source.
Working Principle of Radiation Pyrometers
The pyrometer is designed so that the radiated heat emitted
from the hot body (whose temperature is to be determined) is focused on the hot
junction of the thermocouple. In this way, all the reflected heat is absorbed
by the hot junction. The cold junction is kept permanently at a low
temperature. The difference in temperature between the two junctions produces a
thermoelectric EMF in the thermocouple. Its value will be equal to one-fourth
or fourth (14) power of hot body temperature. This principle is stated by
Stephen Boltzmann Law of Radiation:
The effect emitted by a hot black body corresponds to
one-fourth of its absolute temperature.
Uses of Radiation Pyrometers
- Radiation pyrometers are commonly used to measure temperatures above 900 ° C.
- These pyrometers can be used in addition to quantifying instruments as well as recording instruments.
- They are mostly used to cover the temperature of the furnace.
Disclaimer
Here are all the details of Pyrometers related to
instrumentation technology. You can read all the original information about
pyrometers here.
If you have any suggestions or complaints, you can
contact us through the website.
www.factsaboutworlda2z.website
Thanks For Reading.
www.factsaboutworlda2z.website




4 Comments
Please write a article on thermocouple.
I will write a article on Thermocouple.