This article covers Tachometers and all types of Tachometers. The use of Tachometers, working principle, and structure are also
explained in detail.
Tachometers
Tachometers are used to measure the rotational speed
(angular velocity) of motors, generators, and other rotating machines. These
are called tachometers. A tachometer is also called a speedometer or speed
counter.
Types of Tachometers
1. Mechanical Tachometers
2. Electrical Tachometers
- DC Generator Tachometers
- AC Generator Tachometers
- Induction Tachometers
- Eddy-Current Tachometers
- Drag Cup Tachometers
3. Electronic Tachometers
- Tooth Rotor tachometers
- Photo-Electric Tachometers
- Stroboscopic Tachometers
Mechanical Tachometers
Mechanical tachometers are used to count and collect the
number of cycles, instead of expressing the speed of a shaft in RPM, with the
help of various gears or wheels or drums, or special mechanical mechanisms. That
is why they are also called registers. A typical example of a mechanical
counter is the mechanical counter. This type of counter is also used in energy
meters, vehicle pedometers, and industry.
Working Principle
In mechanical counters, several gears, cogwheel wheels, or
solid toothed drums are attached in such a way that the movement of one wheel
moves the rest of the wheels in a certain proportion.
Construction
A toothed wheel type counter has three, four, or five wheels
with ten teeth. Each wheel or drum is numbered from 0 to 9. And these wheels
(or drums) are locked together in a case in such a way that only one digit of
it is on the harrow (or drum) in the window in front of the box. Is visible
from. Figure (a) shows a mechanical stroke type counter. It is also called a
Ratchet Type counter. With ten strokes, its unit drum (or wheel) completes one
cycle (0 to 9 digits).
 |
| Tachometers |
Before one cycle of the unit drum is completed, the other
drum rotates up to one digit through a transfer mechanism attached to the drum.
Thus, after completing ten cycles of the first drum, the second drum (which is
called the tenth drum or 10th drum in English). A spinning wheel. Similarly,
after completing ten cycles of the second drum, one cycle of the third (100th
drum) is completed. Figure (b) shows a rotary counter used in industry (six
digits). It is used to count the number of cycles in its unit time with the
shaft or spindle of continuously rotating low and medium-speed machines. To its
right is a knob resetting the numbers.
Electrical Tachometers
Electrical tachometers operate using electric current or
voltage. There are three types of this.
DC Generator Tachometers
As the name suggests, these tachometers are small DC
generators, commonly used to measure the speed of a rotating machine (such as a
motor, etc.).
Working Principle
This tachometer shows the speed of a rotating machine in
terms of the value of the voltage generated inside it, i.e. the shaft of the
machine whose speed is to be determined is connected to this tachometer. As a
result, the armature of the tachometer is rotated and calibrated at a direct
speed instead of the voltage directly proportional to the speed of the rotating
machine.
Construction and working
The DC generator tachometer is a DC generator with a
permanent magnet. The shaft of its armature (rotating part of DC generator) is
attached to the shaft of this machine. Whose speed is measured.
Due to the permanent magnet, its magnetic field is also
constant. Therefore, if the speed of the armature is low then the low voltage
is produced, and if its speed is high then the output voltage also increases.
The generator is designed in such a way that it produces even a small amount of
voltage at its maximum speed. The speed of a rotating machine is measured by
giving the voltage generated by the jester a millivoltmeter which is directly
calibrated in RPM. Usually, the generator and speed indicator meter are
enclosed in the same shell. The figure shows the internal structure of a DC
generator tachometer.
 |
| DC Tachometers |
AC Generator Tachometers
The AC generator tachometer was built because of the
problems found in the DC generator tachometer. So there are solid connections
for the speed indicator. The rotor in the tachometer of the AC generator can be
permanent magnetic or electromagnetic. And the rotor is rotated by touching the
shaft, the speed of which has to be measured. This meter is most popular due to
its accuracy, high efficiency, and extremely low maintenance.
Working Principle
The operation of this tachometer depends on the speed of
rotation of a machine and the amount of voltage generated in it or the
frequency of the input voltage. The speed of measurement is known.
Construction and working
The structure of this tachometer is almost like that of an
AC generator. This tachometer consists of a rotating or rotating magnetic
field. Which is a permanent magnet or electromagnet. What is winded on the coil
coaster? The shaft of the machine whose speed is to be determined is connected
to the rotor of the tachometer. The rotation of the shaft of the rotating
machine rotates the parameters of the tachometer, resulting in the induction of
the stator coil to produce EMF.
Electronic Tachometers
Calibration of the electronic tachometer is easy and output
can be carried far and wide. There are the following types.
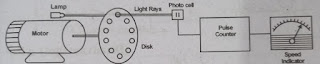
Photo Electric tachometers
A photoelectric tachometer is an instrument in which the
speed of a rotating machine is calculated using an electronic counter in the
form of pulses with the help of light.
Working Principle
The operation of this instrument depends on the
photoelectric effect. Under which when light falls on a photocell, an
alternating voltage is generated in it. The speed of a rotating machine is determined
by measuring them. This light falling on the photocell comes through a
perforated disk attached to the shaft of the rotating machine.
Construction and Working
This tachometer consists of a non-transparent disk. This
disk is mounted on the shaft of a rotating machine, the speed of which has to
be measured. This disk has holes on all sides near the outer edge. At some
distance behind the disc, a small lamp is fitted in the alignment of the holes
in such a way that when the holes come in front of it, its light passes through
the hole and falls on a light sensor on the other side. This light sensor is a
photovoltaic cell.
 |
| Electric Tachometers |
Thanks For Reading.